
A colonoscopy is a procedure by which a doctor will closely look into your large intestine, known as the colon, and your rectum. It is done using a long, thin, flexible tube called a colonoscope, with a tiny camera and light at its tip. As the tube moves gently through the bowel, the camera sends clear images to a monitor to help the doctor find everything that looks unusual, such as polyps, swelling, bleeding, or early signs of cancer.
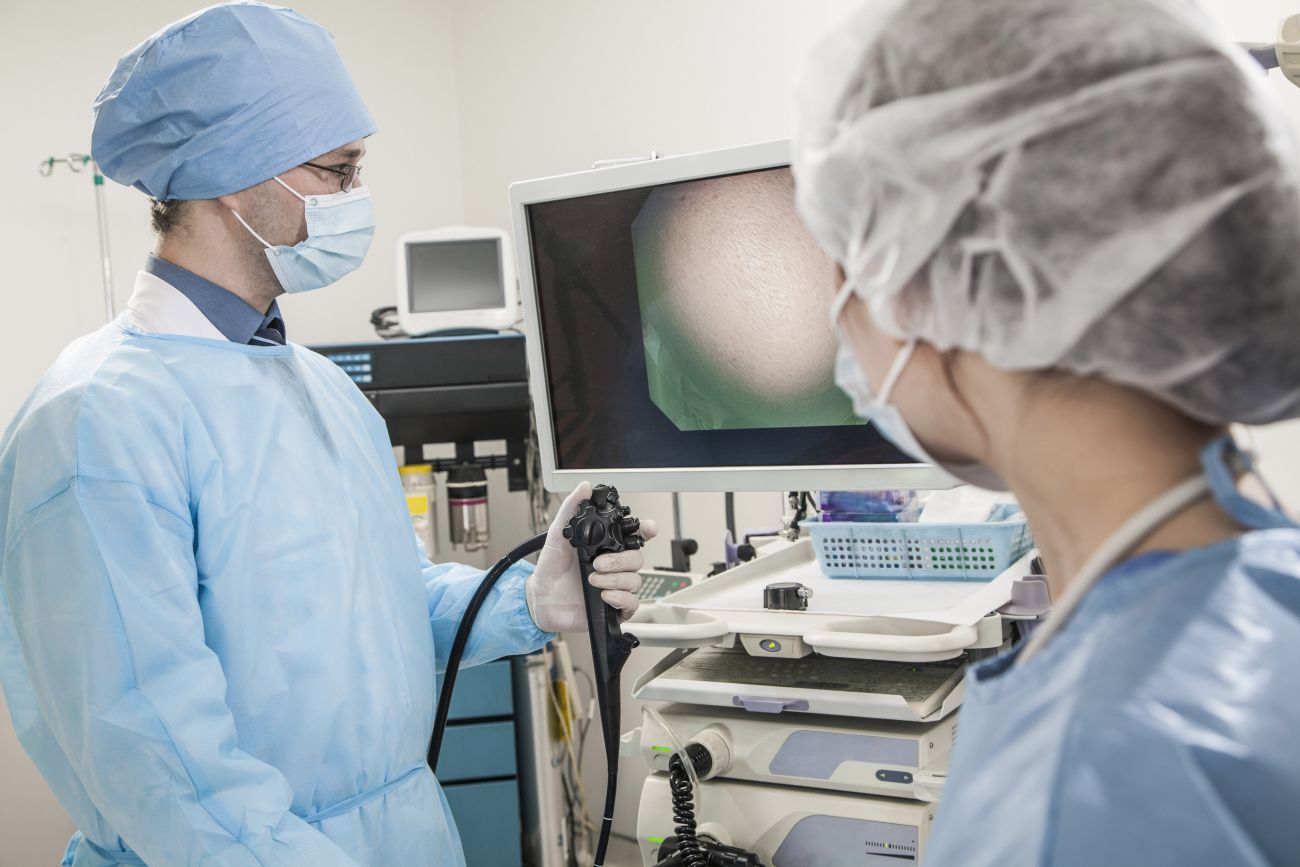
Most patients feel minimal discomfort as sedation is used. Some may experience mild cramping or bloating.
You need to follow a clear liquid diet and take prescribed bowel-cleansing medications as instructed by your doctor.
The procedure usually lasts 30–60 minutes, but total time in the clinic may be longer due to preparation and recovery.
Yes, small polyps can be removed safely during the procedure and sent for further analysis.
Screening intervals depend on age, family history, and previous findings, but generally, it is recommended every 5–10 years for average-risk adults.