
An Upper GI Endoscopy, or esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD), is an easy, safe procedure that your doctor may use to visually examine the upper part of your intestinal system: the esophagus, stomach, and the beginning of the small intestine, or duodenum.
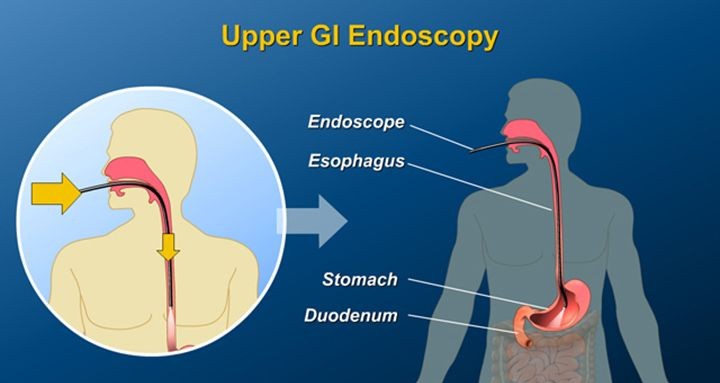
Normally, this test takes place with mild sedation and, therefore, is painless and comfortable for the patient. It gives important information unavailable with X-rays or scans, which helps in the proper diagnosis and early treatment of digestive disorders.
Upper GI Endoscopy, also called Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD), is a procedure that uses a flexible tube with a camera (endoscope) to examine the esophagus, stomach, and the first part of the small intestine.
Doctors usually recommend it for patients with persistent heartburn, difficulty swallowing, unexplained abdominal pain, vomiting, bleeding, or to investigate ulcers, gastritis, or suspected cancers.
The procedure usually takes between 45 minutes to 2 hours. Most patients stay in the hospital for 1–2 days and can return to normal activities within a few days.
You will be asked to fast (no food or drink) for at least 6–8 hours before the procedure. Inform your doctor about any medications, allergies, or existing health conditions before the test.
No, it is not usually painful. A local anesthetic spray is applied to the throat and sedation may be given. You might feel slight pressure or discomfort, but most patients tolerate it well.