
Dr. Piyush Gupta is a highly regarded liver specialist in North Delhi, known for his expertise in managing and treating liver fibrosis. With extensive experience in gastroenterology and liver disorders, he provides individualized care focused on reducing liver scarring, improving liver function, and preventing further damage. Dr. Gupta uses advanced diagnostic tools and evidence-based therapies to support long-term liver health and recovery.
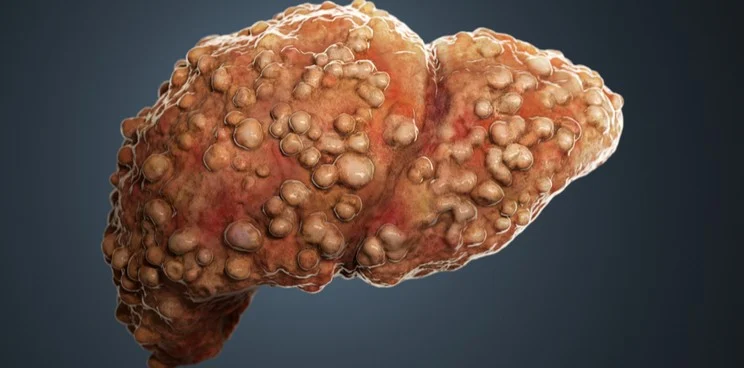
Liver fibrosis is a condition where healthy liver tissue is gradually replaced by scar tissue due to long-term damage. This scarring affects the liver’s structure and reduces its ability to function properly. Over time, it can hinder essential processes like detoxification and protein production, making early detection crucial for maintaining liver health.
Doctors usually diagnose liver fibrosis using blood tests, imaging scans like FibroScan or ultrasound, and sometimes a liver biopsy to assess the extent of scarring.
People with chronic hepatitis, heavy alcohol consumption, fatty liver disease, or genetic liver conditions are more likely to develop fibrosis over time.
No, they are not the same. Liver fibrosis is an early stage of scarring, while cirrhosis is a more advanced stage where severe scarring permanently affects liver function.
Yes. Since the liver helps filter toxins and supports metabolism, damage to it can affect digestion, hormone balance, and even the immune system over time.
Yes, long-term use of certain drugs or exposure to toxins can damage liver cells, leading to fibrosis. It’s always best to take medicines as prescribed and under medical supervision.